The numerator is the odds in the intervention arm. The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome.

Absolute Risk Reduction Arr Is The Absolute Difference Between The Control Event Rate And The Experimental Event Rate Arr Is U Reduction Prevention Outcomes
Odds Ratio Odds of Event A Odds of Event B.

. If the probability of an event is 080 80 then the probability that the event will not occur is 1-080 020 or 20. A risk ratio 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group. Relative risk A AB C CD In short heres the difference.
Indeed whenever p is small the probability and odds will be similar. If the probability of an event occurring is Y then the probability of the event not occurring is 1-Y. The 95 confidence intervals and statistical.
RR aabccd acdcab. The odds ratio OR is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group. The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds yep its that obvious whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities.
The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group. The risk ratio or relative risk is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event see Box 92a. An odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group.
So here the probability 01 and the odds 0111 are quite similar. And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group. The odds of an event of interest occurring is defined by odds p 1-p where p is the probability of the event occurring.
Now we can relate the odds for males and females and the output from the logistic regression. Lets look at an example. An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds.
In our example above p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk. The odds of an event represent the ratio of the probability that the event will occur probability that the event will not occur. It is undefined if p 2 q 1 equals zero ie if p 2 equals zero or q 1 equals zero.
That reduced risk is 1-odds so will be 30 percent reduced risk fo exposure. So if p01 the odds are equal to 01090111 recurring. A risk ratio.
For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions. In this newsletter we will review the definitions of risk ratios and odds ratios compare the two statistics and discuss the situations in which each is appropriate. Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program.
Previous article Next article Keywords epidemiology measures of effect number needed to treat. If the risk ratio is 1 or close to 1 it suggests no difference or little difference in risk incidence in each group is the same. OR abcd adbc The risk ratio RR also called the relative risk is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in non-smokers.
For example we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball. The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds. Relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities.
The risk difference is 050 040 010 ie an absolute increase in survival of 10 which translates into a number needed to treat of 10 ie 1the risk difference or. No difference in risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR 1. Risk difference is an absolute measure of effect and it is calculated by subtracting the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals from that of unexposed.
An RR or OR more than 10 indicates an increase in risk or odds among the exposed compared to the unexposed whereas a RR or OR. For example if survival is 50 in one group and 40 in another the measures of effect or association are as follows. Risk difference is an absolute measure of effect and it is calculated by subtracting the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals from that of unexposed.
The relative risk is also called the risk ratio. Risk odds1 odds odds risk1 risk Deeks. The odds ratio OR is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in non-smokers.
An RR or OR of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk or odds between the groups being compared. Statistical significance is linked to the p-value or CI- which. Odds refer to the ratio of the probability of an event occurring to the probability of it not occurring within a group.
The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is 32771774 32747717 1809. Increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR 1. OR.
It is calculated as. OR 044 and RR 089. So when researchers calculate an odds ratio they do it like this.
If the risks were 08 and 09 the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers. OR1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome. The risk ratio the incidence rate ratio and the odds ratio are relative measures of effect.
Odds can also be defined as the risk or probability of an event occurring over the risk of the event being absent Scott 2008Odds and risks can sometimes be computed through the following formulae. A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk. The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined.
The risk ratio the incidence rate ratio and the odds ratio are relative measures of effect. Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR 1. An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups.
So the odds for males are 17 to 74 the odds for females are 32 to 77 and the odds for female are about 81 higher than the odds for males. The denominator is the odds in the control or placebo arm Odds Ratio OR So if the outcome is the same in both groups the ratio will be 1 which implies there is no difference between the two arms of the study. The risk ratio is 050040 125 ie a relative increase in survival of 25.
OR1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome. OR 0752 and RR 075. In a control group.
Oddsevent Pevent happens 1-Pevent happens For example the odds of picking a green ball are 02 1-02 02 08 025. Lower risk protective in risk of group 1 compared to 2 In our example p 1 proportion of women receiving SAT p 2 proportion of men receiving SAT OR pp pp pp pp 11 22 12 21 1. If the Odds ratio is 07 then it indicates a protective effect - Ie a reduced odds of exposure in case vs control group.
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk. The distinction between risk ratios and odds ratios can be confusing and researchers are often not sure which one is the appropriate statistic for their study. The more common the disease the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk.
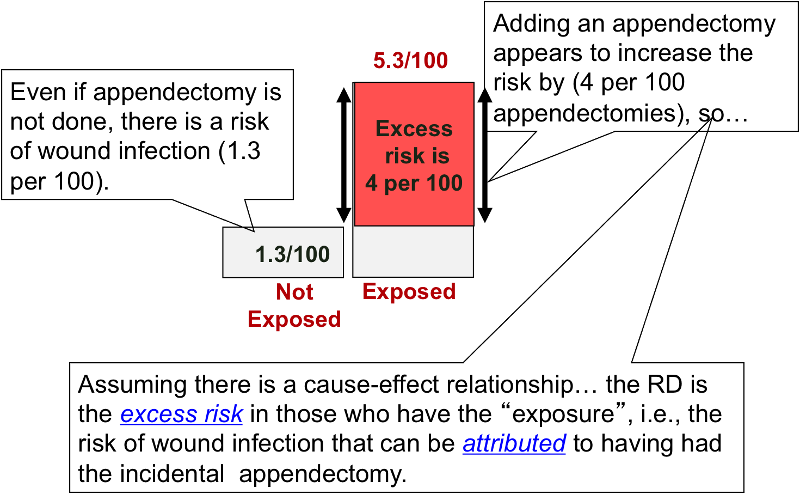
Risk Differences And Rate Differences
What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
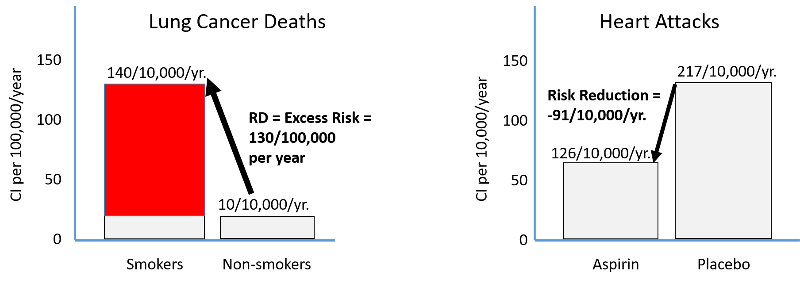
Risk Ratio And Risk Difference

How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
0 Comments